Stories focus on everyday matters affecting our bodies, such as pills, carbs and viruses, then lead on to some of the biological concepts that underlie them – like enzymes, nerves and DNA.

2.35 Self-discipline and laziness
What psychology and neuroscience have to tell us.

2.34 The origins of inequality
Spending, saving and the roots of wealth inequality

The science behind this universal drive

2.32 Ultra Processed Food – part II Additives
Explanation of emulsifiers, antioxidants and other food additives

2.31 Ultra Processed Food – part I Background
What we learn from a book by Chris van Tulleken about the battle between the food industry and healthy eating.

What brain science and psychology can tell us about how we regulate our desires
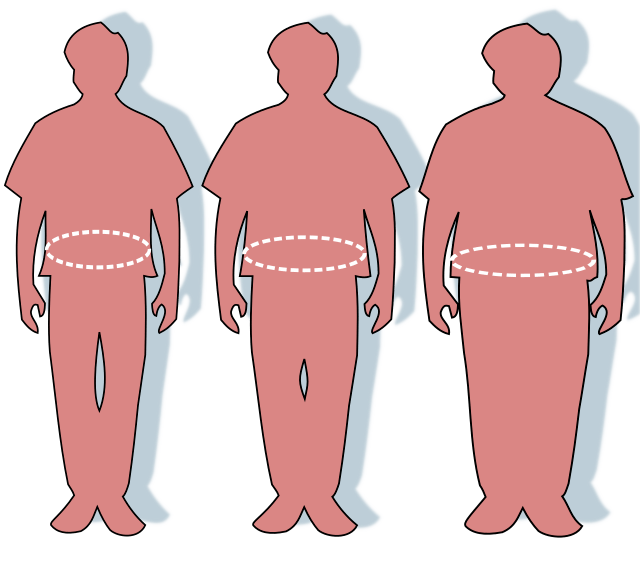
2.29 How drugs work: ozempic, aspirin and more
The roles of design and chance in drug discovery

What research in anthropology, archaeology, psychology and neuroscience tell us about adolescence.

The cells and molecules that help us lift, push, pull …and sneeze!

2.26 A trip down the alimentary canal
How we digest our food
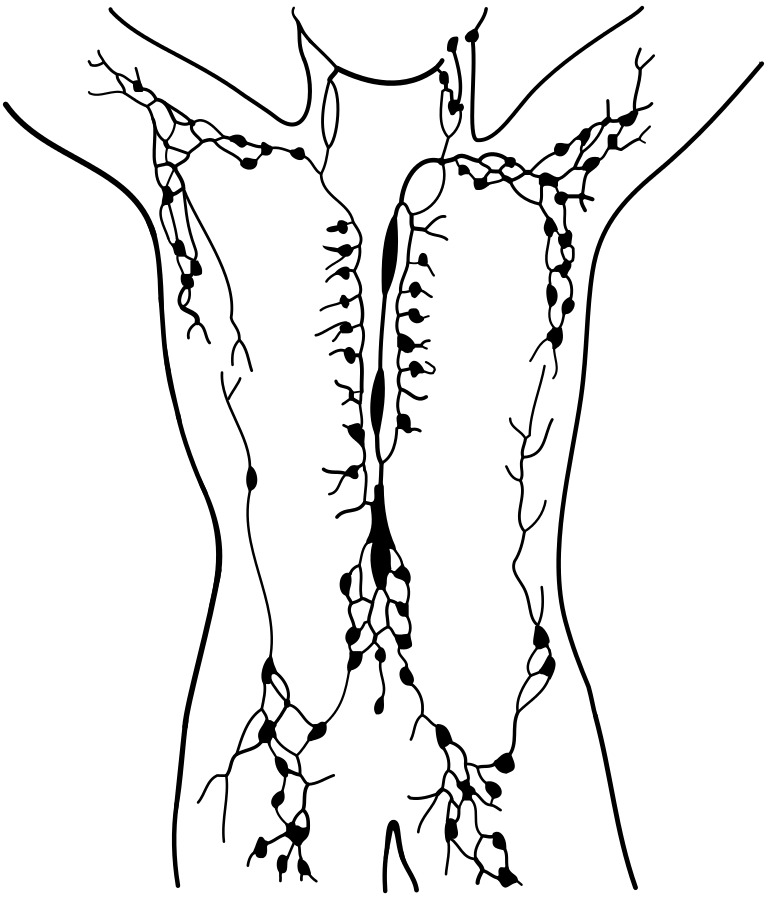
2.25 Lymph, blood and hormones: body systems
Systems reach across the body, supporting the work of the organs
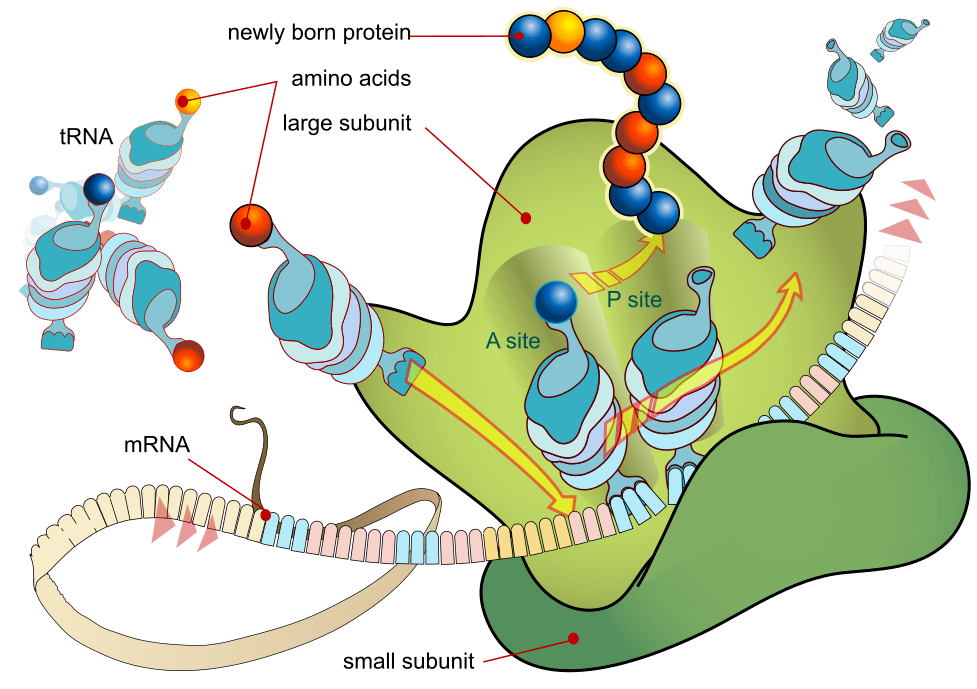
2.24 Imagining impossible things
Making sense of the microscopic in the body and the gigantic in the unverse

A story of migration, hibernation, gloom and renewal

The contribution of neuroscience, psychology and evolutionary biology to our understanding of aggression and collaboration
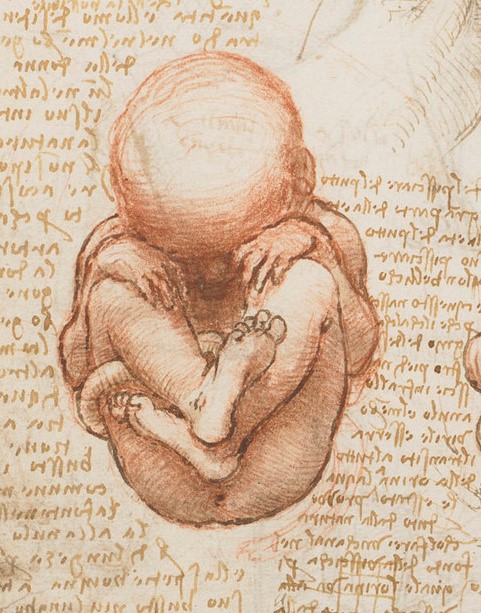
2.21 How we grow – from embryo to adult
The story of cells as they multiply and the molecules that instruct them

What we can learn from global surveys and research on hormones, genes and the brain
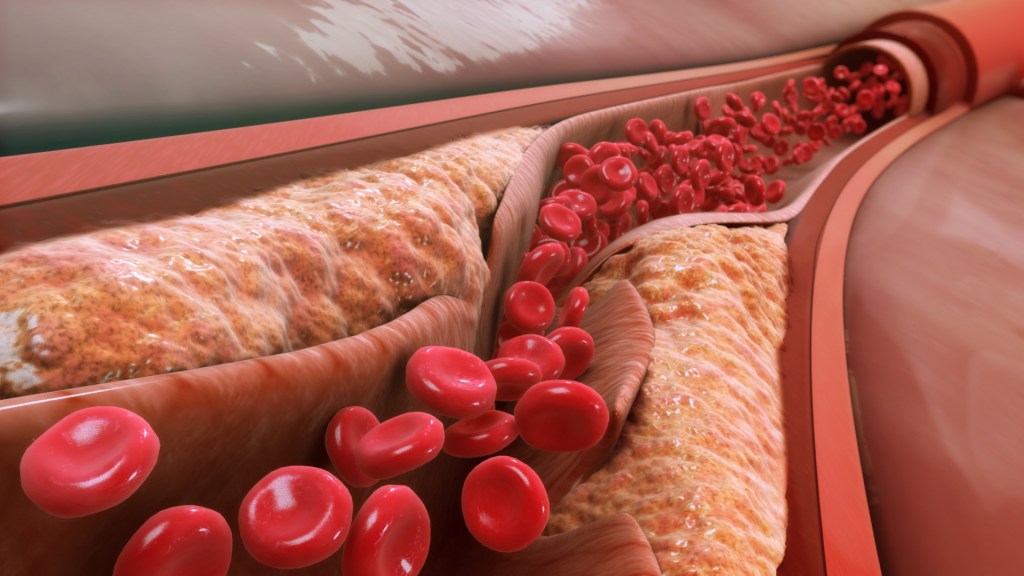
2.19 Ailments of the heart and blood system
What goes wrong and how it’s treated
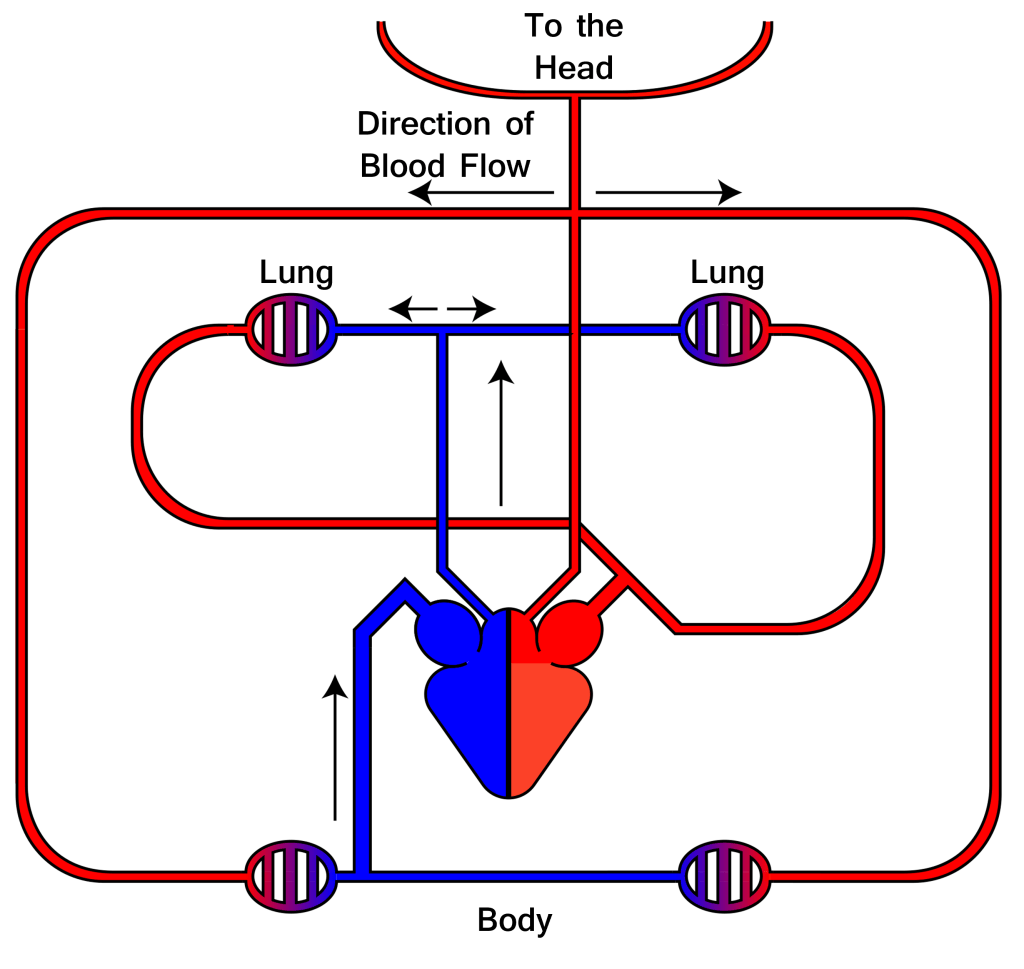
2.18 The heart and blood system
How the system works
What it is and how it works (or fails to)

The brain science of sleep, dreams and emotion

The story of ‘malaise’: runny nose, fatigue, aches and pains

2.14 Species, breeds and cultivars
Chromosomes, genes and the taxonomic hierarchy

2.13 It’s in the genes: why we look like our parents – a bit
The genetics of inheritance
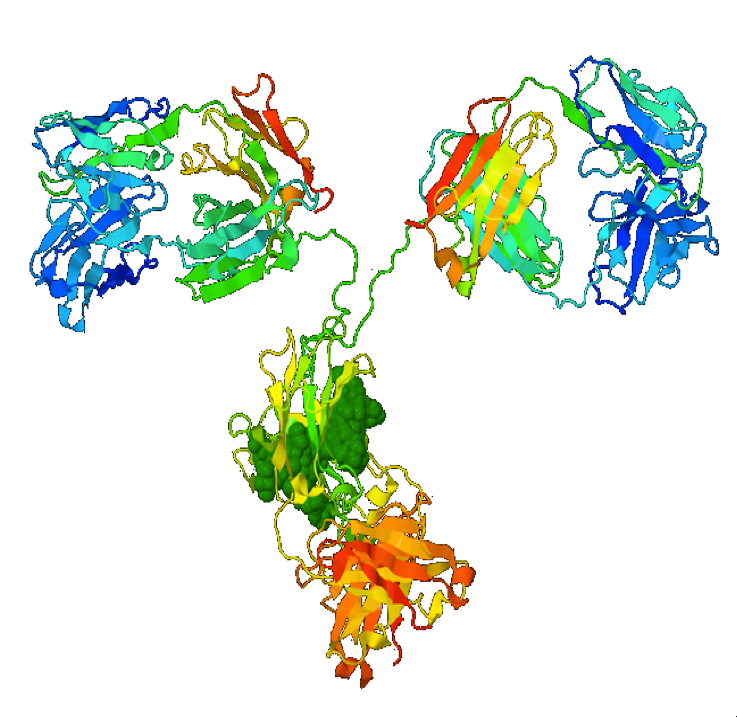
2.12 Immunity, vaccines and variants
The immune system and how vaccines stimulate it
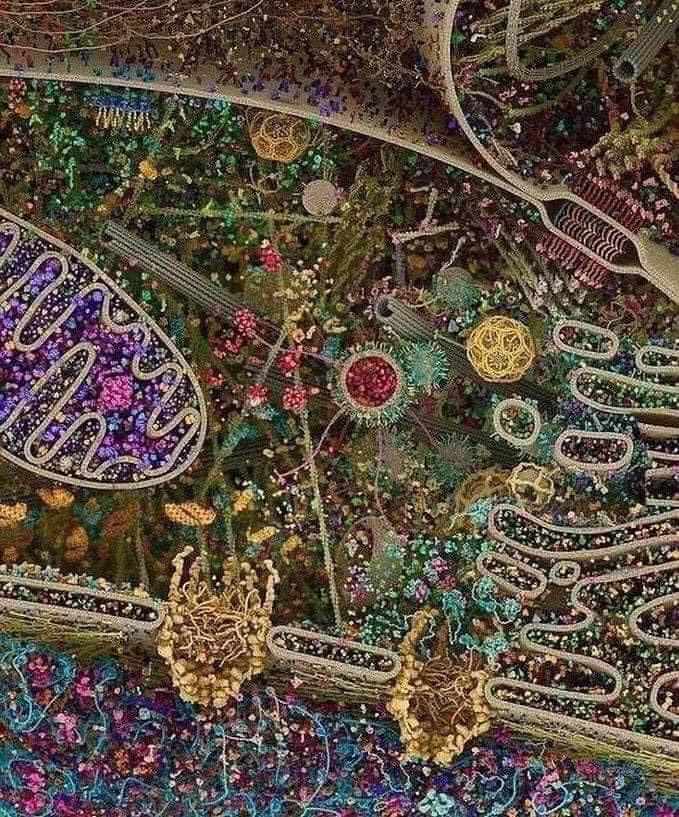
2.11 Very small and very busy: life inside the cell
What goes on inside our human cells?

2.10 Drug and vaccine development
How scientists go about developing new drugs and vaccines
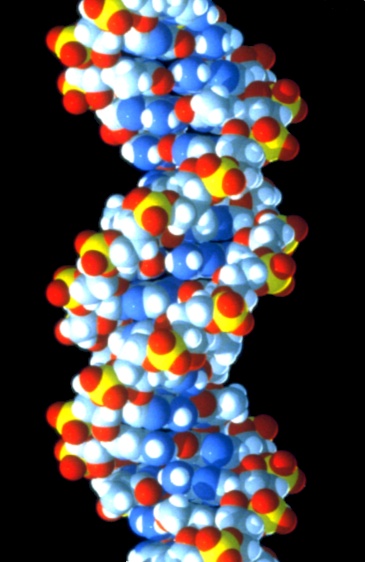
2.9 Mutation, genes and proteins
How genes provide the code for making proteins
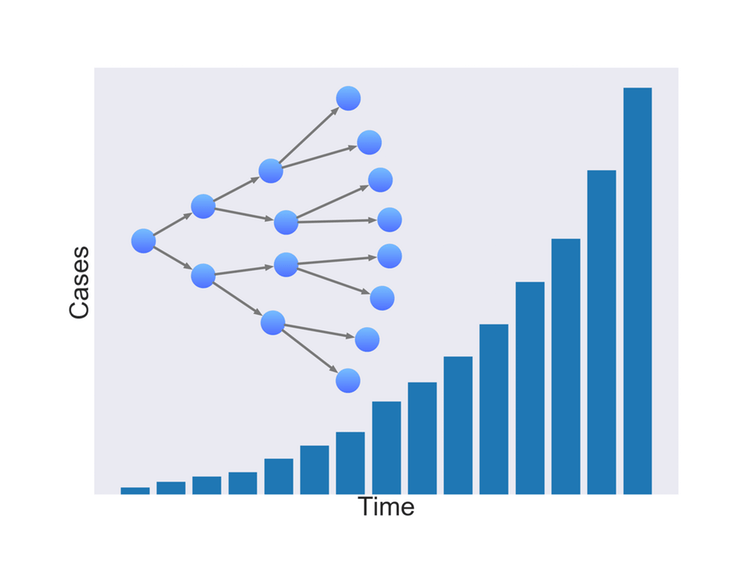
2.8 COVID-19 part 2: epidemics, protection and social behaviour
How epidemics grow and people respond
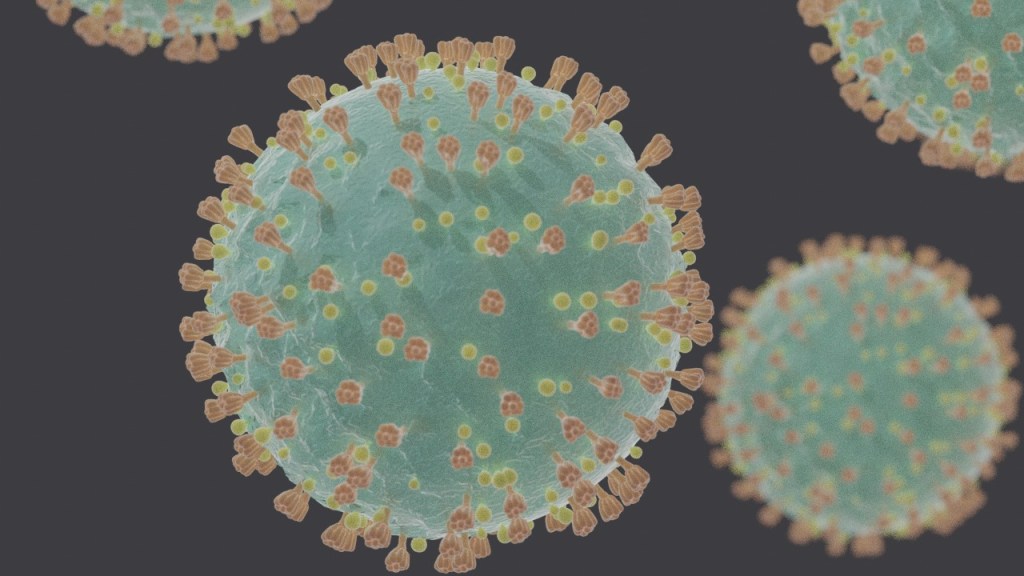
2.7 COVID-19 part 1: Viruses, Lungs and Vaccines
The basic science of the Covid-10 pandemic

2.6 Sugar, carbs and type-2 diabetes
Investigating the substances behind the surge in diabetes 2
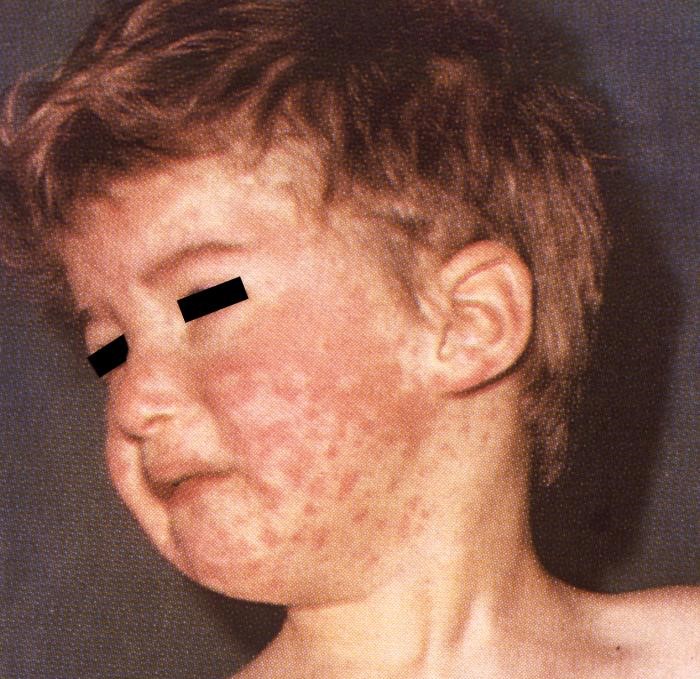
2.5 Vaccination and antibodies
What are antibodies and how does vaccination bring them on?

Familiar to dieters, brewers and cheesemakers, but what are they?

2.3 Brain, behaviour and learning
How the brain influences the way we learn and behave
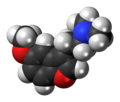
2.2 Depression: the vital role of serotonin
The role the vital serotonin molecule plays in our nervous system
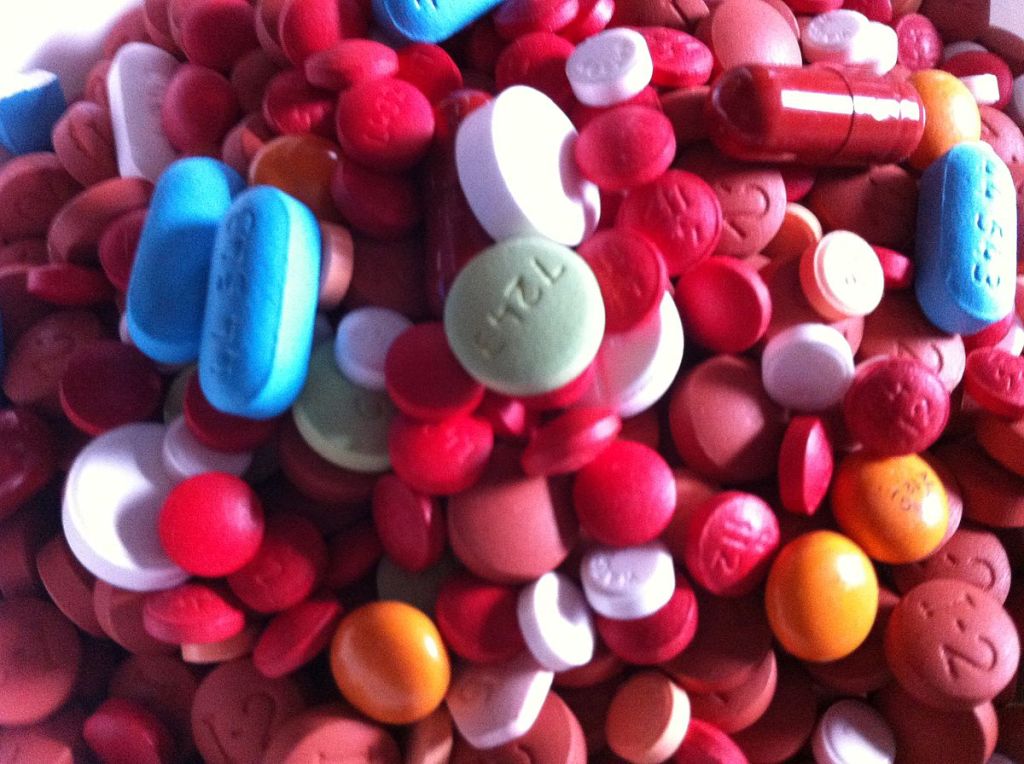
2.1 How do pills know where to go?
The shape and nature of drug molecules dictate where they act
